In the era of digital content creation, links and images are fundamental elements for building rich, interactive documents. Markdown, as a lightweight markup language, provides concise yet powerful syntax for creating and managing these multimedia elements. Whether you're a technical writer, blogger, open-source project maintainer, or content creator, mastering Markdown's link and image capabilities is a crucial skill for enhancing content quality and user experience.
This guide takes you on an in-depth exploration of the complete world of Markdown links and images, from basic syntax to advanced application techniques, platform-specific features to performance optimization, offering a comprehensive and practical learning resource. Through numerous examples, best practices, and troubleshooting tips, we'll help you become an expert in Markdown multimedia content.
Why Are Links and Images So Important?
In modern content creation, plain text alone no longer meets user needs. Links provide navigation and reference capabilities, enabling readers to easily access related resources, delve deeper into specific topics, or quickly jump within documents. Images add visual appeal to content, conveying information more intuitively, showcasing product features, or explaining complex concepts.
Content marketing research shows that articles containing images receive 94% more views than plain text articles [1]. Meanwhile, a well-structured internal linking system not only enhances user experience but also significantly improves search engine optimization [2]. For technical documentation, clear link structures and appropriate image captions are particularly important for ensuring accurate information delivery.
Markdown's design philosophy achieves a perfect balance between simplicity and readability. Compared to HTML, Markdown's link and image syntax is more intuitive and easier to remember while maintaining sufficient flexibility for various application scenarios. This simplicity allows content creators to focus on the content itself rather than complex markup syntax.
Learning Path Planning
This guide adopts a progressive learning approach, starting with fundamental concepts and gradually advancing to sophisticated applications and professional techniques. Each chapter includes detailed syntax explanations, practical examples, and useful tips to ensure you can systematically master all knowledge points.
For beginners, we recommend starting with the Basic Syntax Mastery chapter, focusing on inline links, image embedding, and basic formatting techniques. Users with some foundation can directly jump to the Advanced Application Techniques chapter to learn reference-style links, responsive images, and custom styling.
If you're looking for platform-specific solutions, the Platform Feature Comparison chapter provides detailed compatibility information and platform-specific functionalities. For professional users handling large volumes of multimedia content, the Performance Optimization and Tool Automation chapter will help establish efficient workflows.
Before starting, we recommend preparing a Markdown-enabled editor with preview functionality, such as Visual Studio Code, Typora, or online editors like ToMarkdown.org, allowing you to view syntax effects in real-time and deepen understanding through practice.
Mastering Basic Syntax
Mastering the basic syntax of Markdown links and images is the first step toward creating high-quality documents. While these syntax elements may appear simple, they contain rich functionalities and nuances. A thorough understanding of these fundamentals will lay a solid foundation for advanced applications.
Detailed Link Syntax
Markdown offers multiple ways to create links, each with specific use cases and advantages. Understanding these different link types and their appropriate applications is key to becoming a Markdown expert.
Inline Links
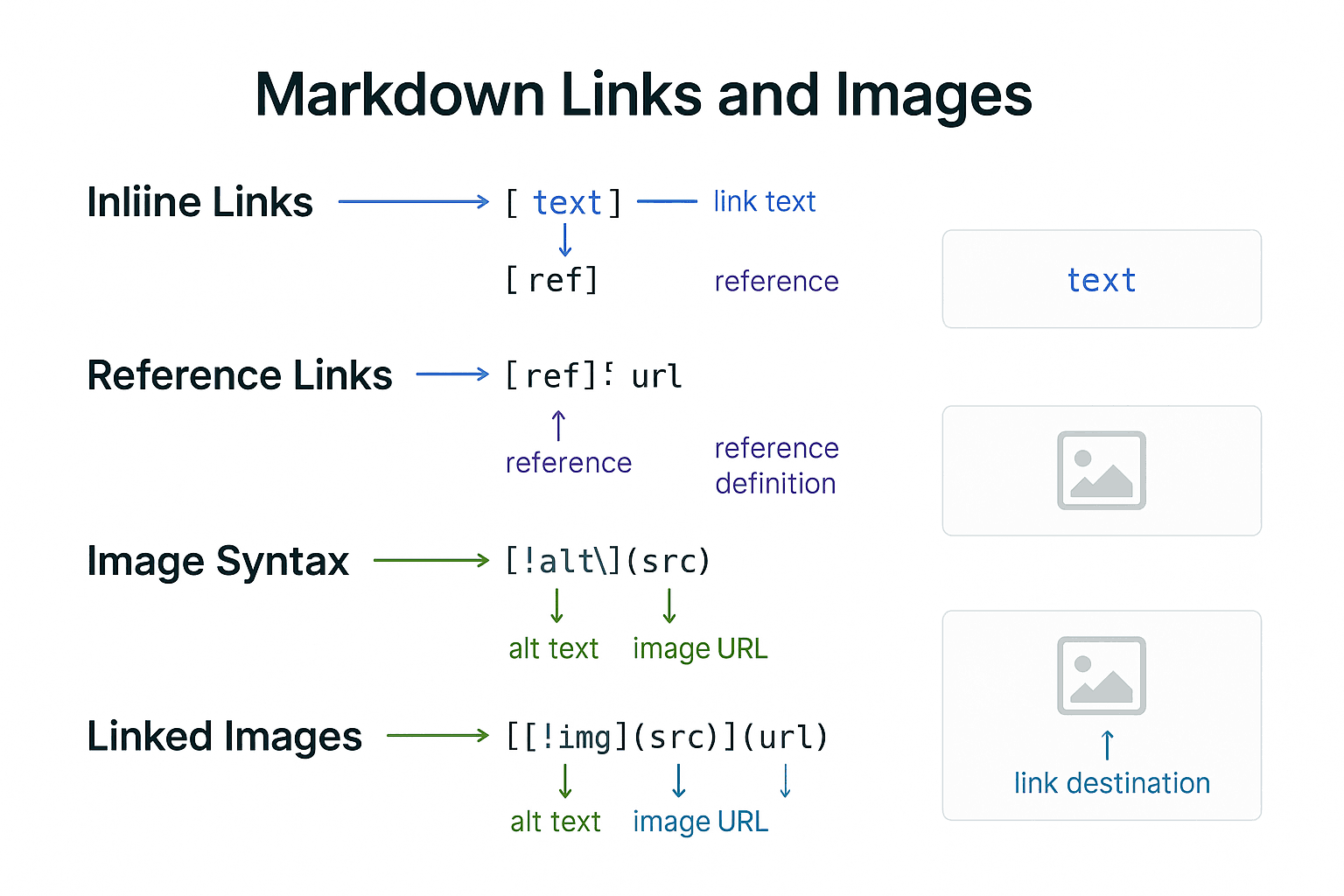
Inline links are the most commonly used form, featuring concise and intuitive syntax suitable for most daily scenarios. The basic syntax is [link text](URL "optional title"), where the link text is the clickable text displayed to users, URL is the target address, and the optional title appears on hover.
[Visit ToMarkdown.org](https://www.tomarkdown.org "Best online Markdown editor")
[GitHub Homepage](https://github.com)
[Contact Us](mailto:[email protected] "Send email")
The advantage of inline links lies in their intuitiveness and self-contained nature. When reading Markdown source code, you can immediately see the link destination, which greatly aids document maintenance and collaboration. However, when documents contain numerous long URLs, inline links may affect source code readability.
In practice, inline links are particularly suitable for: short documents, temporary links, external resource references, and social media links. For technical documentation, inline links are commonly used for API references, tool links, and quick access to related resources.
Reference-Style Links
Reference-style links separate link definitions from link usage, improving document readability and maintainability. This approach is especially suitable for long documents with numerous links or situations requiring multiple references to the same link.
This is a link to [ToMarkdown.org][1], and here's another to [GitHub][github].
You can also use [implicit link labels][], where the link text serves as the label itself.
[1]: https://www.tomarkdown.org "Best online Markdown editor"
[github]: https://github.com "World's largest code hosting platform"
[implicit link labels]: https://example.com
Key advantages of reference-style links include: improved source code readability, easier link management, support for link reuse, and simplified handling of long URLs. In academic writing, technical documentation, and lengthy articles, reference-style links are the preferred solution.
Automatic Links
For simple URLs and email addresses, Markdown supports automatic linking. Simply enclose the URL or email address in angle brackets to create a clickable link.
<https://www.tomarkdown.org>
<[email protected]>
Automatic links are suitable for scenarios requiring full URL display, such as API endpoints in technical documentation, configuration file examples, or reference material lists.
Internal Links
Internal links enable navigation within the same document, which is crucial for user experience in lengthy documents. Markdown supports linking to headings, custom anchors, and document fragments.
[Jump to Basic Syntax](#mastering-basic-syntax)
[View Advanced Techniques](#advanced-application-techniques)
[Return to Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
Anchor generation rules vary by platform but generally follow these principles: convert headings to lowercase, replace spaces with hyphens, and remove special characters. Understanding your target platform's anchor generation rules is essential for creating reliable internal links.
Detailed Guide to Image Syntax
Images are indispensable elements in modern documentation. Markdown's image syntax maintains simplicity while offering rich functionality to meet various display needs.
Basic Image Embedding
Markdown image syntax closely resembles link syntax, with the addition of an exclamation mark. The basic format is .



The alt text provides a description when the image fails to load and is crucial for screen readers and SEO. The optional title appears on hover, offering additional context or explanations.
Reference-Style Images
Similar to links, images also support reference-style syntax, which is particularly useful for reusing images or managing large collections.
![ToMarkdown.org Interface Screenshot][screenshot]
![Feature Demo][demo]
[screenshot]: markdown_image_techniques.png "ToMarkdown.org User Interface"
[demo]: markdown_links_images_cheatsheet.png "Feature Demonstration"
Linked Images
Using images as links is a common requirement, especially for creating galleries, product showcases, or click-to-zoom functionality. The syntax involves wrapping the image syntax within link syntax.
[](markdown_image_techniques.png "View Full Size")
[](https://www.tomarkdown.org "Visit Official Site")
Path and URL Handling
Properly handling image and link paths is essential for ensuring documents display correctly. Understanding the differences between relative paths, absolute paths, and URLs—and how they behave in various environments—is critical for creating portable documents.
Relative Paths
Relative paths locate resources based on the current document's position, making them the most common choice, especially for internal project references.



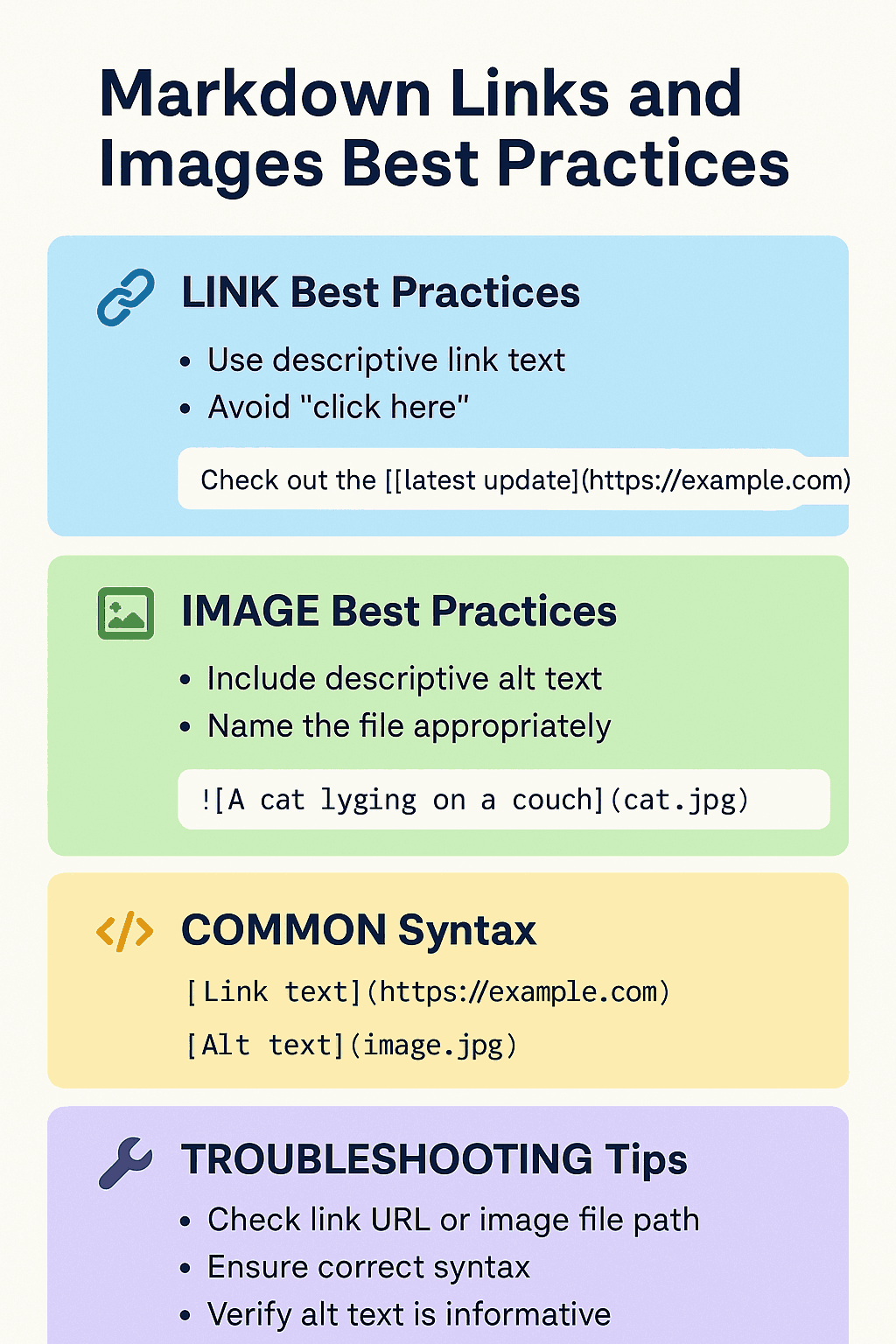
Advantages of relative paths include better project portability, compatibility with version control, and suitability for offline viewing. However, note that relative paths may behave differently across viewing environments, particularly on platforms like GitHub or GitLab.
Absolute Paths and URLs
Absolute paths start from the root directory, while URLs point to web resources. These methods are ideal for referencing external assets or ensuring consistent access across environments.



When using absolute paths and URLs, consider factors like network dependency, loading speed, caching policies, and link validity. For critical image assets, it's advisable to use reliable CDN services or localize the resources.
Common Mistakes and Solutions
When learning Markdown link and image syntax, beginners often encounter some typical issues. Understanding these common errors and their solutions can help you avoid frustration and quickly improve your skills.
Syntax Errors
The most frequent mistakes include mismatched brackets, missing exclamation marks, improper spacing, and special character escaping issues.
<!-- Incorrect Examples -->
[Link text(https://example.com) <!-- Missing closing square bracket -->
 <!-- Spaces in link text -->
<!-- Correct Examples -->
[Link text](https://example.com)

[Link text](https://example.com)
Path Issues
Path errors are a primary cause of broken links and missing images. Common problems include case sensitivity, path separators, encoding issues, and relative path baselines.
<!-- Mind the case sensitivity -->
 <!-- May fail on some systems -->

<!-- Mind the path separators -->
 <!-- May fail on other systems -->

Special Character Handling
When URLs or filenames contain special characters, proper escaping or encoding is required.
<!-- Filenames with spaces -->


<!-- URLs with special characters -->
[Search results](https://example.com/search?q=markdown%20guide)
By thoroughly understanding these fundamental syntax rules and common pitfalls, you now possess the ability to create basic links and images. Next, we will explore more advanced techniques to help you craft more professional and flexible multimedia content.
Advanced Techniques
After mastering the basics, the next step is to learn how to apply advanced techniques to create more professional and adaptable multimedia content. These skills will help you handle complex layout requirements, optimize user experience, and fully leverage the advantages of modern web technologies.
HTML Enhancements
While Markdown is designed for simplicity, there are cases where finer control is needed. Most Markdown processors support embedded HTML, offering limitless possibilities for extension.
Image Size Control
Standard Markdown syntax does not support direct image dimension specification, but we can use HTML's <img> tag for precise control.
<img
src="https://www.tomarkdown.org/logo.png"
alt="ToMarkdown.org Logo"
width="300"
height="200"
/>
<img
src="markdown_image_techniques.png"
alt="Responsive Image"
style="max-width: 100%; height: auto;"
/>
<img
src="markdown_links_images_cheatsheet.png"
alt="Small Icon"
style="width: 32px; height: 32px; vertical-align: middle;"
/>
This approach is particularly useful for scenarios requiring exact control over image display, such as product showcases, technical documentation illustrations, and user interface screenshots.
Image Alignment and Layout
Using CSS styles, we can achieve various image alignment effects to create more professional document layouts.
<!-- Center alignment -->
<div style="text-align: center;">
<img src="banner.jpg" alt="Banner image" style="max-width: 100%;" />
</div>
<!-- Left float -->
<img
src="avatar.jpg"
alt="Avatar"
style="float: left; margin: 0 15px 15px 0; width: 150px;"
/>
<!-- Right float -->
<img
src="sidebar-image.jpg"
alt="Sidebar image"
style="float: right; margin: 0 0 15px 15px; width: 200px;"
/>
Responsive Images
In modern web development, responsive design is crucial. We can use HTML5's <picture> element and srcset attribute to create images that adapt to different devices.
<picture>
<source media="(max-width: 768px)" srcset="mobile-image.jpg" />
<source media="(max-width: 1024px)" srcset="tablet-image.jpg" />
<img
src="desktop-image.jpg"
alt="Responsive image"
style="width: 100%; height: auto;"
/>
</picture>
Advanced Linking Techniques
Anchor Links and Page Navigation
In long documents, a well-structured navigation system is essential for user experience. In addition to linking to headings, we can also create custom anchors.
<!-- Create a custom anchor -->
<a id="custom-anchor"></a>
<!-- Link to the custom anchor -->
[Jump to custom position](#custom-anchor)
<!-- Smooth scrolling effect -->
<a href="#section1" style="scroll-behavior: smooth;">Smooth scroll</a>
External Link Optimization
For external links, we can add additional attributes to improve user experience and security.
<a href="https://external-site.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">
Open external link in a new window
</a>
target="_blank" opens the link in a new window, while rel="noopener noreferrer" provides security by preventing the new page from accessing the original page's window object.
Download Links
When linking to downloadable files, use the download attribute to specify the filename.
<a href="document.pdf" download="User Manual.pdf">Download User Manual</a>
<a href="data.json" download>Download Data File</a>
Multimedia Content Integration
Video Embedding
Although Markdown itself does not support video, we can embed video content in various ways.
<!-- HTML5 video -->
<video controls style="width: 100%; max-width: 800px;">
<source src="demo.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
<source src="demo.webm" type="video/webm" />
Your browser does not support video playback.
</video>
<!-- YouTube embed -->
<iframe
width="560"
height="315"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/VIDEO_ID"
frameborder="0"
allowfullscreen
>
</iframe>
Audio Content
Audio files can be embedded similarly to videos, with multiple formats for compatibility.
<audio controls>
<source src="podcast.mp3" type="audio/mpeg" />
<source src="podcast.ogg" type="audio/ogg" />
Your browser does not support audio playback.
</audio>
Interactive Content
For content requiring interactivity, embed iframes or enhance functionality with JavaScript.
<!-- Embedding online tools -->
<iframe
src="https://www.tomarkdown.org/editor"
width="100%"
height="500"
frameborder="0"
>
</iframe>
<!-- Collapsible content -->
<details>
<summary>Click to expand details</summary>
<p>This is detailed content, hidden by default and revealed upon clicking.</p>
</details>
Platform Feature Comparison
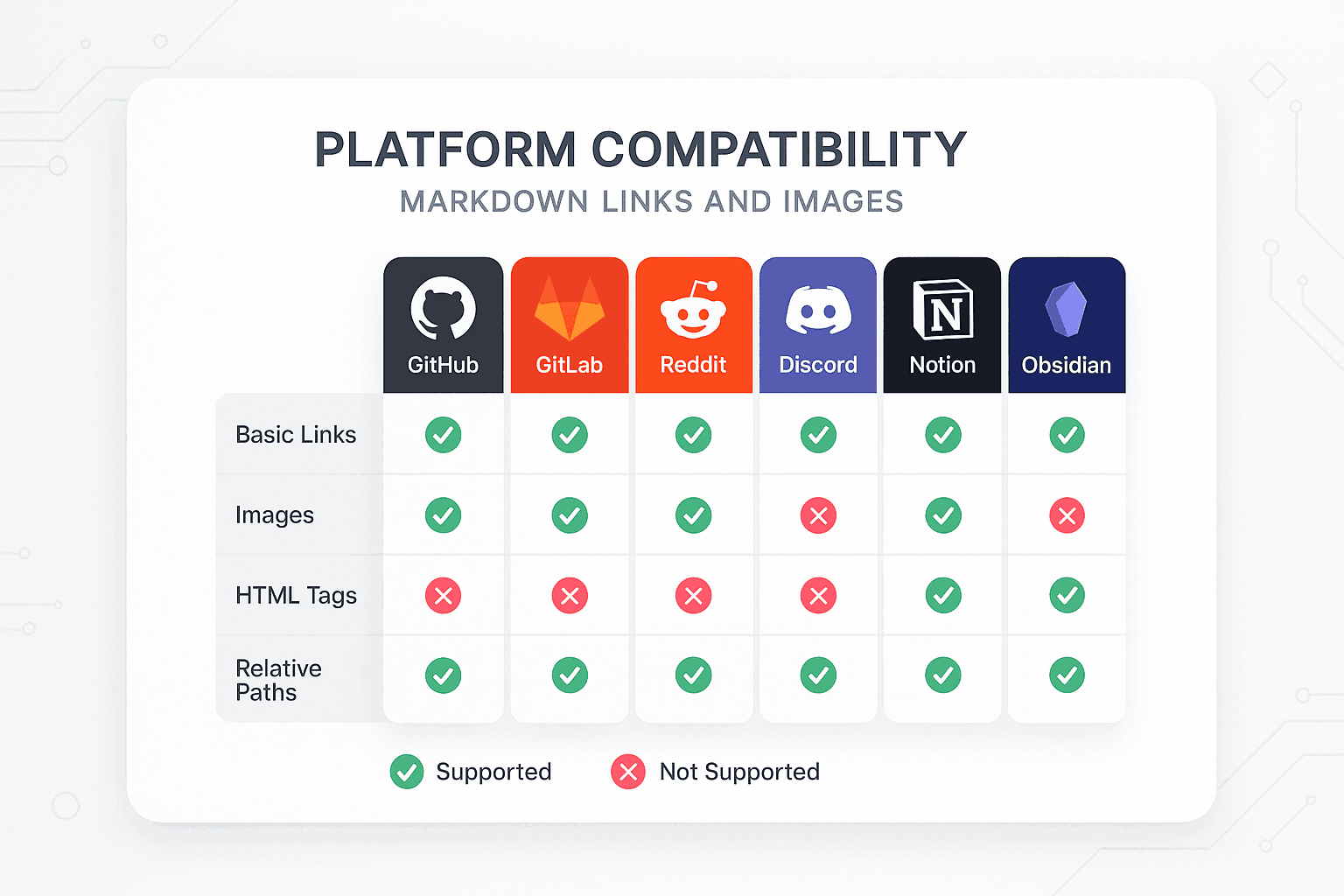
Different Markdown processors and platforms vary in their support for links and images. Understanding these differences is crucial for creating cross-platform compatible documents.
GitHub Flavored Markdown (GFM)
GitHub, the most popular code hosting platform, extends standard Markdown with its GFM features.
Unique Features
<!-- Automatic link detection -->
Visit https://github.com for more information.
<!-- Strikethrough -->
~~This text is deleted~~
<!-- Task lists -->
- [x] Completed task
- [ ] Pending task
<!-- User and issue references -->
@username mentioned issue #123
Image Handling
GitHub has special processing for images, including auto-scaling, click-to-zoom, and relative path resolution.
<!-- GitHub automatically handles large images -->

<!-- Relative paths are based on repository root -->

GitLab Features
GitLab offers some unique features, particularly in project management and collaboration.
<!-- Quick actions -->
/assign @username
/label ~bug ~priority::high
<!-- Diagram support -->
```mermaid
graph TD
A[Start] --> B[Process]
B --> C[End]
```
Other Platform Differences
Notion
Notion supports rich multimedia content and database integration.
<!-- Database embedding -->
[Database view](notion://www.notion.so/database-id)
<!-- Page references -->
[[Page Title]]
Obsidian
Obsidian focuses on knowledge management with powerful linking and graph features.
<!-- Bidirectional links -->
[[Related Note]]
<!-- Note embedding -->
![[Other Note]]
<!-- Image resizing -->

Practical Application Examples

Theoretical knowledge needs to be reinforced and deepened through practical application. Below are some typical use cases demonstrating how to effectively utilize Markdown's link and image features in real-world projects.
Technical Documentation Writing
Technical documentation is one of the most important applications of Markdown. A well-structured linking system and appropriate use of images can significantly enhance the usability of documents.
API Documentation Example
# User API Reference
## Retrieve User Information
**Endpoint:** `GET /api/users/{id}`
**Parameters:**
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
| ---- | ------- | -------- | ---------------------- |
| id | integer | Yes | Unique user identifier |
**Response Example:**
```json
{
"id": 123,
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
```
**Related Links:**
- [User Authentication](auth.md#user-authentication)
- [Error Handling](errors.md)
- [Online API Testing Tool](https://www.tomarkdown.org/api-tester)

Installation Guide Example
# Software Installation Guide
## System Requirements
Before starting installation, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 10+ / macOS 10.14+ / Ubuntu 18.04+
- Memory: At least 4GB RAM
- Storage: 500MB available space
## Installation Steps
### 1. Download Installation Package
Visit the [official download page](https://example.com/download) to download the installation package for your system.

### 2. Run the Installation Program
Double-click the downloaded installation package and follow the wizard to complete installation.

### 3. Verify Installation
Open terminal or command prompt and run the following command to verify installation:
```bash
software-name --version
```
If you see version information, installation was successful.
## Troubleshooting
If you encounter problems, please refer to:
- [Frequently Asked Questions](faq.md)
- [Community Support Forum](https://community.example.com)
- [Submit Bug Report](https://github.com/example/software/issues)
Blog and Content Marketing
In blog writing, the use of links and images directly affects reader experience and SEO effectiveness.
Blog Post Example
# 10 Markdown Tips to Boost Your Productivity

In today's fast-paced work environment, mastering efficient document writing techniques is crucial. Markdown, as a lightweight markup language, helps us quickly create formatted documents. This article shares 10 practical Markdown tips to significantly enhance your productivity.
## 1. Use Keyboard Shortcuts for Faster Writing
Most Markdown editors support keyboard shortcuts. For example, in [ToMarkdown.org](https://www.tomarkdown.org "Best online Markdown editor"):
- `Ctrl+B`: Bold text
- `Ctrl+I`: Italic text
- `Ctrl+K`: Insert link

## 2. Use Templates for Consistency
Creating document templates ensures format consistency and saves repetitive work time.
```markdown
# Project Report Template
## Project Overview
[Project description]
## Current Progress
[Current status]
## Next Steps
[Future plans]
```
**Related Reading:**
- [Markdown Best Practices Guide](best-practices.md)
- [Efficient Document Management Strategies](document-management.md)
- [Team Collaboration Tools Recommendations](collaboration-tools.md)
---
_This article was originally published on [My Blog](https://myblog.com), please cite the source when reposting._
Project Documentation Management
Both open-source and enterprise projects require comprehensive documentation systems, and reasonable link structures help users quickly find needed information.
README File Example
# Project Name
[](https://github.com/user/repo/actions)
[](https://github.com/user/repo/releases)
[](LICENSE)
Concise and clear project description explaining the main features and purpose.

## Features
- ✅ Feature One: Detailed description
- ✅ Feature Two: Detailed description
- ✅ Feature Three: Detailed description
## Quick Start
### Installation
```bash
npm install project-name
```
### Basic Usage
```javascript
const project = require("project-name");
project.doSomething();
```
## Documentation
- 📖 [Complete Documentation](docs/README.md)
- 🚀 [Quick Start Guide](docs/getting-started.md)
- 📚 [API Reference](docs/api.md)
- 💡 [Example Code](examples/)
## Contributing
We welcome all forms of contributions! Please read the [Contributing Guide](CONTRIBUTING.md) for details.
## License
This project is licensed under the [MIT License](LICENSE).
## Contact Us
- 🐛 [Report Issues](https://github.com/user/repo/issues)
- 💬 [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/user/repo/discussions)
- 📧 [Email Contact](mailto:[email protected])
Tools and Automation
Efficient tools and automated workflows can significantly improve the creation and maintenance efficiency of Markdown documents. Below are some recommended tools and techniques.
Editors and Plugins
Visual Studio Code
VS Code is one of the most popular Markdown editors with a rich plugin ecosystem.
Recommended Plugins:
- Markdown All in One: Provides shortcuts, table of contents generation, and math formula support
- Markdown Preview Enhanced: Enhanced preview functionality with chart and slideshow support
- Paste Image: Quick paste and image insertion
- markdownlint: Syntax checking and formatting
Configuration Example:
{
"markdown.preview.breaks": true,
"markdown.preview.linkify": true,
"markdown.preview.typographer": true,
"[markdown]": {
"editor.wordWrap": "on",
"editor.quickSuggestions": false
}
}
Online Editors
For users who don't want to install software, online editors are excellent choices:
- ToMarkdown.org: Full-featured online Markdown editor
- Dillinger: Simple online editor supporting multiple export formats
- StackEdit: Online editor with sync and collaboration support
Image Management Tools
Image Compression and Optimization
Use online image compression tools like TinyPNG:
# Using ImageOptim (macOS)
imageoptim *.png *.jpg
# Using TinyPNG API
curl --user api:YOUR_API_KEY \
--data-binary @input.png \
--output output.png \
https://api.tinify.com/shrink
Batch Processing Scripts
#!/bin/bash
# Batch convert image formats and sizes
for file in *.png; do
# Convert to WebP format
cwebp -q 80 "$file" -o "${file%.png}.webp"
# Generate thumbnails
convert "$file" -resize 300x300 "thumb_$file"
done
Link Checking and Maintenance
Automated Link Checking
// Using Node.js to check link validity
const axios = require("axios");
const fs = require("fs");
async function checkLinks(markdownFile) {
const content = fs.readFileSync(markdownFile, "utf8");
const linkRegex = /\[([^\]]+)\]\(([^)]+)\)/g;
const links = [];
let match;
while ((match = linkRegex.exec(content)) !== null) {
links.push({
text: match[1],
url: match[2],
line: content.substring(0, match.index).split("\n").length,
});
}
for (const link of links) {
try {
await axios.head(link.url, { timeout: 5000 });
console.log(`✅ ${link.url}`);
} catch (error) {
console.log(`❌ ${link.url} (line ${link.line})`);
}
}
}
checkLinks("README.md");
GitHub Actions Automated Checking
# .github/workflows/link-check.yml
name: Link Check
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
link-check:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Check Links
uses: gaurav-nelson/github-action-markdown-link-check@v1
with:
use-quiet-mode: "yes"
use-verbose-mode: "yes"
config-file: ".github/workflows/mlc_config.json"
Performance Optimization
When dealing with large numbers of images and links, performance optimization becomes crucial. Below are some practical optimization strategies.
Image Optimization Strategies
Format Selection
Different image formats are suitable for different scenarios:
| Format | Best For | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photos, complex images | Small file size, good compatibility | Lossy compression |
| PNG | Icons, simple graphics | Lossless compression, transparency support | Larger file size |
| WebP | Modern browsers | High compression, good quality | Limited compatibility |
| SVG | Vector graphics | Scalable, small file size | Not suitable for complex images |
Responsive Image Implementation
<!-- Using srcset for multiple sizes -->
<img
src="image-800.jpg"
srcset="image-400.jpg 400w, image-800.jpg 800w, image-1200.jpg 1200w"
sizes="(max-width: 600px) 400px,
(max-width: 1000px) 800px,
1200px"
alt="Responsive image"
/>
<!-- Using picture element -->
<picture>
<source media="(max-width: 600px)" srcset="mobile.webp" type="image/webp" />
<source media="(max-width: 600px)" srcset="mobile.jpg" />
<source srcset="desktop.webp" type="image/webp" />
<img src="desktop.jpg" alt="Image description" />
</picture>
Lazy Loading
<!-- Native lazy loading -->
<img src="image.jpg" loading="lazy" alt="Lazy loaded image" />
<!-- Using Intersection Observer API -->
<script>
const images = document.querySelectorAll("img[data-src]");
const imageObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
const img = entry.target;
img.src = img.dataset.src;
img.classList.remove("lazy");
observer.unobserve(img);
}
});
});
images.forEach((img) => imageObserver.observe(img));
</script>
CDN and Caching Strategies
CDN Configuration
Using CDN can significantly improve image loading speed:
<!-- Using CDN to host images -->

<!-- Using GitHub as free CDN -->

Cache Optimization
<!-- Set cache headers -->
<meta http-equiv="Cache-Control" content="max-age=31536000" />
<!-- Use version numbers to avoid cache issues -->

Troubleshooting Guide
Even experienced users may encounter various issues. Below are common problems and their diagnostic solutions.
Link Issues Diagnosis
Broken Links
Symptoms: Unable to access the target page when clicking a link
Possible Causes:
- URL spelling error
- Target page deleted or moved
- Network connection issues
- Permission restrictions
Solutions:
# Test link using curl
curl -I https://example.com/page
# Check DNS resolution
nslookup example.com
# Use online tools for checking
# https://httpstatus.io/
Relative Path Issues
Symptoms: Links behave inconsistently in different environments
Solutions:
<!-- Avoid using root directory references for relative paths -->
❌ [Link](/docs/guide.md)
<!-- Use paths relative to current file -->
✅ [Link](../docs/guide.md)
<!-- Or use complete URLs -->
✅ [Link](https://github.com/user/repo/blob/main/docs/guide.md)
Image Display Issues
Images Not Displaying
Common causes and solutions:
<!-- Check file path -->
❌  <!-- Case sensitive -->
✅ 
<!-- Check file extension -->
❌  <!-- Missing extension -->
✅ 
<!-- Check special characters -->
❌  <!-- Space issue -->
✅ 
✅ 
Image Size Issues
<!-- Control maximum width -->
<img
src="large-image.jpg"
style="max-width: 100%; height: auto;"
alt="Large image"
/>
<!-- Fixed dimensions -->
<img src="icon.png" width="32" height="32" alt="Icon" />
<!-- Responsive handling -->
<img
src="image.jpg"
style="width: 100%; max-width: 600px; height: auto;"
alt="Responsive image"
/>
Platform Compatibility Issues
GitHub Special Handling
<!-- GitHub relative paths are based on repository root -->

<!-- Use raw.githubusercontent.com to ensure image display -->

Different Platform Differences
<!-- Use universal syntax -->
✅ [Link](https://example.com)
✅ 
<!-- Avoid platform-specific syntax -->
❌ [[Internal link]] <!-- Obsidian specific -->
❌ @username <!-- GitHub specific -->
Best Practices Summary
Through this guide, you have mastered the complete knowledge system of Markdown links and images. Below are some key best practices to help you achieve optimal results in practical applications.
Content Organization Principles
- Clear Structure: Use meaningful filenames and directory structures
- Orderly Links: Establish a logically clear navigation system
- Image Optimization: Choose appropriate formats and dimensions
- Compatibility First: Use standard syntax to ensure cross-platform compatibility
Maintenance and Updates
- Regular Checks: Use automated tools to verify link validity
- Version Control: Track document changes and image updates
- Backup Strategy: Ensure the availability of critical resources
- Performance Monitoring: Focus on loading speed and user experience
Team Collaboration
- Unified Standards: Develop team-wide Markdown writing guidelines
- Tool Consistency: Use the same editors and plugins
- Resource Management: Create a shared image and asset repository
- Document Review: Establish content review and quality control processes
By following these best practices, you will be able to create high-quality, easily maintainable Markdown documents that deliver an excellent reading experience for users.
References
[1] Content Marketing Institute. "Visual Content Marketing Statistics." 2024. https://contentmarketinginstitute.com/visual-content-statistics
[2] Moz. "Internal Linking for SEO: A Complete Guide." 2024. https://moz.com/learn/seo/internal-link
[3] CommonMark Specification. "CommonMark Spec." 2024. https://spec.commonmark.org/
[4] GitHub. "GitHub Flavored Markdown Spec." 2024. https://github.github.com/gfm/
[5] Mozilla Developer Network. "HTML img Element." 2024. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/img
[6] W3C. "HTML5 Picture Element Specification." 2024. https://www.w3.org/TR/html-picture-element/
[7] Google Developers. "Web Performance Best Practices." 2024. https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance
[8] Markdown Guide. "Extended Syntax." 2024. https://www.markdownguide.org/extended-syntax/
[9] GitLab. "GitLab Flavored Markdown." 2024. https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/markdown.html
[10] Accessibility Guidelines. "Alt Text Best Practices." 2024. https://webaim.org/techniques/alttext/
About ToMarkdown.org
ToMarkdown.org is a professional online Markdown conversion toolkit that effortlessly transforms HTML, URLs, and Word documents into standard Markdown format. It intelligently recognizes document structures, fully preserves original formatting, and supports GFM syntax, making document conversion simple and efficient. Whether you're a beginner or a professional user, ToMarkdown.org meets all your Markdown writing needs.
Recommended Articles: